| Strain Name |
NOD.CB17-Prkdcscid Il2rgtm1Bcgen/Bcgen |
Common Name |
B-NDG mice |
| Background |
NOD-scid |
Catalog number | 110586 |
| Aliases |
Male: Prkdc (-/-), Il2rg (X-/Y); Female: Prkdc (-/-), Il2rg (X-/X-) |
||
|
NCBI Gene ID |
16186 | ||
(Click for Chinese Version)
Background
The immunodeficient B-NDG mice (NOD.CB17-Prkdcscid Il2rgtm1Bcgen/Bcgen) was independently designed and generated by Biocytogen. B-NDG mice were generated by deleting the Il2rg gene from NOD scid mice with severe immunodeficient phenotype. This mouse model lacks mature T cells, B cells and functional NK cells. It is internationally recognized as an immunodeficient mouse model well suited for human-derived tissue or cell engraftment.
- NOD (non-obese diabetes) genetic background: Spontaneous type I diabetes; defective function of T cells, NK cells, macrophages, and dendritic cells and lack hemolytic function of complement.
- Prkdc (protein kinase, DNA activated, catalytic polypeptide) gene mutation: no mature T cells and B cells, severe combined immunodeficiency (scid) of cellular and humoral immunity.
- Il2rg gene knockout: the gamma chain of IL2 receptor (IL2Rγc, CD132) is located on the X chromosome of mouse, and is the common receptor subunit of cytokines IL2, IL4, IL7, IL9, IL15 and IL21 with important immune functions. The immune function of Il2rg knockout mice was severely reduced, especially the activity of NK cells was almost lost.
B-NDG mice: Combined NOD scid-Il2rg null background features, severe immunodeficient phenotype, absence of mature T cells, B cells, and functional NK cells, decreased function of macrophages and dendritic cells. It is very suitable for the transplantation of human hematopoietic stem cells (CD34+ HSCs) and peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) to obtain humanized mice with human immune system.
• The highest degree of immunodeficiency among all immunodeficient mouse models
• Longer lifespan than NOD scid mice; 1.5 years on average
• Minimal to absent rejection of human-derived cells and tissues
• More efficient for CDX and PDX model generation
Major Applications
• Human-derived cell or tissue engraftment
• Tumor and tumor stem cell research
• ES and iPS cell research
• Hematopoiesis and immunology studies
• Human infectious disease studies
• Development of new humanized mouse models

Animal breeding and maintenance
B-NDG mice are housed in isolators instead of IVCs in our facility. Based on our experience, the mice can live up to 2 months in SPF standard IVCs. This time frame matches the requirements of most experiments performed with B-NDG mice. To improve facility standards, strict sanitation procedures are recommended: cages and bedding need to be sterilized by autoclaving or Co60 irradiation before use, and cages need to be changed in laminar flow hoods weekly. Keeping a clean, high standard housing environment helps to improve the life span of B-NDG mice.

Animal breeding and maintenance
Transportation
Biocytogen’s B-NDG mouse can be shipped using land and/or air. Although the courier is notified to handle the crate with care, stress response of mice during shipment is still inevitable. Although enough supply of water jelly and food will be provided in cages, increased metabolism and fecal excretion caused by the stress may result in dehydration and loss of body weight. General percentage weight loss due to shipment is ~10%. The percentage can be as high as 15% if the shipment procedure is longer and the cage is populated. Usually, the most of the lost body weight is regained (although cannot reach 100%) after 5-7 days of adaptive feeding (Labdiet food is recommended)).

Phenotypic analysis

Complete loss of T, B and NK cells in B-NDG mice. Blood, spleen and bone marrow were collected from C57BL/6, NOD scid and B-NDG mice (female, 6-week-old, n=3). Leukocyte subpopulations were analyzed by flow cytometry analysis. A. Representative FACS plots. B. Statistical analysis of FACS. Results showed that T cells, B cells and NK cells were detectable in all tissues of C57BL/6 mice. Only NK cells were detectable in blood and spleen of NOD scid mice. But none of the three cells were detectable in any tissue of B-NDG mice.

Analysis of myeloid cells in B-NDG mice. Blood, spleen and bone marrow were collected from C57BL/6, NOD scid and B-NDG mice (female, 6-week-old, n=3). Leukocyte subpopulations were analyzed by flow cytometry analysis. A. Representative FACS plots. B. Statistical analysis of FACS. Results showed that percentages of granulocytes and monocytes/macrophages of blood, spleen and bone marrow in B-NDG mice were relatively higher than that in wild-type C57BL/6 and NOD scid mice. But the percentages of DCs were lower in B-NDG mice than that in wild-type C57BL/6 and NOD scid mice.

Complete loss of antibody production in B-NDG mice. Serum were collected from BALB/c mice and B-NDG mice. 1% BSA was added as control group. Mouse antibodies were detected with ELISA method. (A) Mouse IgG and IgM detection. (B) mouse IgG subclasses detection. Results showed that mouse IgG, IgM and IgG subclasses were detectable in serum of BALB/c mice, but not detectable in serum of B-NDG mice. These results demonstrate a complete loss of antibody production in B-NDG mice.

Histological analysis of mouse spleen. Spleen tissues of C57BL/6, NOD scid and B-NDG mice were respectively subjected to HE staining and immunohistochemical analysis (female, 9-week-old, n=3). (A) Splenic tissue HE staining. The results showed that the splenic structure of C57BL/6 mice was normal and the follicles were clear; The splenic structure of NOD scid mice showed leukopulp hypoplasia; But B-NDG mice showed a complete disappearance of follicular structure. (B) Immunohistochemical analysis of T cells and B cells in spleen. Mouse T cells and B cells were respectively detected with anti-mouse CD3 antibody or anti-mouse CD19 antibody. The results showed that the number and distribution of mCD3+ T cells and mCD19+ B cells in the spleen tissue of C57BL/6 mice were normal (brown); But both T cells and B cells were not detectable in NOD scid mice and B-NDG mice, indicating that there were no T cells and B cells in spleen of NOD scid mice and B-NDG mice.


Survival curve of B-NDG mice. Health status of 50 male and 50 female mice were observed. Results showed that female mice did not die before 12 months of age and the survival rate at 13 months was 86%. One male mouse died at 6 months of age and the survival rate of male mice at 13 months was 70%.

Complete blood count (CBC) of B-NDG mice. Values are expressed as mean ± SD.

Blood biochemical test of B-NDG mice. Values are expressed as mean ± SD.

Average weight of the main organs of B-NDG mice.

Histopathological analysis of organs in B-NDG mice. The main organs of B-NDG mice were isolated at 32 weeks of age and analyzed with HE staining (male, n=15; female, n=16). Results showed that the follicular structure of the spleen of all mice were completely lost. 80% of the male mice had small calcifications in the testicular tissue. No obvious abnormalities were found in other organs (brain, heart, lung, liver, spleen, stomach, small intestine, colon, kidney and ovary).
Successfully establishing a CDX lymphoma model with B-NDG mice

Raji lymphoma cell line can successfully establish hematologic and metastatic mouse tumor model in B-NDG mice. Raji cells (5×105) were injected via tail vein of B-NDG mice, NOD scid mice and BALB/c nude mice. (A) Survival curves of the three strain of mice; (B) Body weight change; (C) The whole blood were collected from the orbital venous plexus of mice every week. Percent of human cells in the whole blood cells were assessed by qPCR; (D) B-NDG mice and NOD scid mice were euthanized and livers were respectively dissected at 18 or 25 days after cell inoculation. (E) Immunohistochemical analysis of human cells in mouse liver and spleen. Human lymphoma cells were detected with anti-human mitochondrial membrane protein antibody. These results showed that CDX mouse model with B-NDG mice had the lowest survival rate, fasted body weight loss compared to the CDX model with nude mice and NOD scid mice. The number of liver metastases in B-NDG mice was significantly higher than that of NOD scid mice. More human lymphoma cells were detected in liver and spleen of B-NDG mice compared to that in NOD scid mice. The results demonstrated that B-NDG mice was the best strain of mice to establish human-derived tumor models compared with nude mice and NOD scid mice.

A Raji lymphoma mouse model was established using B-NDG mice and the efficacy of antibody X was verified. B-luc-GFP Raji cells (5×105) were injected via tail vein of B-NDG mice and divided into 3 groups: no dosing group, day 10 dosing group, day 3 and day 10 dosing group. Both dosing groups were given the same dose of antibody X and tumor growth was observed with imaging at different time points. (A) Imaging of mice to observe tumor growth; (B) Fluorescence intensity curve of tumor cells. The results showed that early antibody therapy (started 3 days after Raji cell transplantation and re-administered 10 days later) was significantly more effective than late antibody therapy (started 10 days after Raji cell transplantation). B-NDG mice is a powerful model for efficacy verification of anti-human antibodies. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.

A Raji lymphoma mouse model was established using B-NDG mice and the efficacy of anti-human CD47 antibodies were verified. B-luc-GFP Raji cells (5×105) were injected via tail vein of B-NDG mice. In vivo imaging systems (IVIS) was used to observe tumor growth. When the fluorescence intensity of the tumor reaches about 1×106 p/sec, the animals were divided into one control group and three treatment group (n=6). (A) Fluorescence intensity curve of tumor cells; (B) Body weight. The results showed that all three anti-human CD47 antibodies could significantly inhibit tumor growth. B-NDG mice is a powerful model for efficacy verification of anti-human CD47 antibodies. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.

A Raji lymphoma mouse model was established using B-NDG mice and the efficacy of anti-human CD47 antibodies were verified. B-luc-GFP Raji cells (5×105) were injected via tail vein of B-NDG mice. In vivo imaging systems (IVIS) was used to observe tumor growth. When the fluorescence intensity of the tumor reaches about 1×106 p/sec, the animals were divided into one control group and three treatment group (n=6). (A) Fluorescence intensity curve of tumor cells; (B) Body weight. The results showed that all three anti-human CD47 antibodies could significantly inhibit tumor growth. B-NDG mice is a powerful model for efficacy verification of anti-human CD47 antibodies. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.

Comparing three cell lines with different Her2 expression level and establishing CDX models in B-NDG mice to verify the difference in efficacy of Her2-targeting ADC drugs. A431, BT-474 and NCI-H1975 cells were implanted subcutaneously in B-NDG mice. Mice were grouped when tumor volume reached to a suitable size, at which time they were treated intravenously with ADC drugs. The drug synthesized internally were marked with “in house”, while the commercial drugs were marked nothing after the drug name. (A) Schematic diagram of CDX model establishment and drug delivery strategy; (B) Expression level of human Her2 in in vitro cultured A431, BT-474, NCI-H1975 cell line; (C) CDX models were established for each of the three cell lines and the efficacy of the Her2-targeting ADC drugs were verified. The results showed that the expression level of human Her2 was high in BT-474 and NCI-H1975 cell line, while the expression level of Her2 in A431 cells was very low. Her2-targeting ADC drugs can significantly inhibit the tumor growth in CDX models established with high-Her2-expressing cell lines (BT-474, NCI-H1975), but had a weak inhibitory effect on low-Her2-expressing tumor (A431). B-NDG mice is a powerful model for efficacy verification of human ADC drugs. Values are expressed as averages ±SEM.

Imaging of orthotopic model for pancreatic cancer by Micro-CT. B-luc MIA Paca-2 cells were orthotopically inoculated into B-NDG mice (n=5). (A) Micro-CT images of orthotopic model in B-NDG mice were scanned from day 14 after inoculation. The images showed the coronal plane of the abdomen, with red areas representing the actual tumor. (B) Tumor growth curve was recorded by contrast-enhanced CT. (C) Dynamic changes of total fluorescence signal in the tumor site after inoculation. The results showed that human pancreatic cancer cell line (B-luc MIA Paca-2 cells) could successfully form tumors in situ pancreas of B-NDG mice.

A MIA Paca-2 pancreatic orthotopic model was established using B-NDG mice and the efficacy of ADC drug was verified. B-luc MIA Paca-2 cells(1E5)were orthotopically implanted into B-NDG mice (female, 7-week-old, n=6). Mice were grouped when imaging signal value reached approximately 7E7 p/sec, at which time they were treated with the ADC drug with different doses and schedules were indicated in panel. (A) Body weight changes during treatment. As shown in panel B, this ADC drug was efficacious but mild, demonstrating that B-luc MIA Paca-2 pancreatic orthotopic model could provide a powerful preclinical model for in vivo evaluation of ADC drug. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.

Engraftment of human PBMCs in B-NDG mice enhances reconstitution of human T cells. Human PBMCs (5E6) were intravenous engrafted into B-NDG mice (female, 6-week-old, n=6). Body weight of each mouse was recorded every week. Death data were collected every day. The peripheral blood was taken at different time points to analyze the reconstitution levels of human immune cells. B-NDG mice showed a high percentage of human CD45+ cells and T cells. B-NDG mice exhibit shortened survival and reduced body weight likely due to GvHD caused by a high Percentages of human T cell reconstitution. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.

A NUGC4 human gastric cancer model was established using human PBMCs engrafted B-NDG mice and the efficacy of anti-human CD3/CLDN18.2 bispecific antibody was verified. Human PBMCs (5E6) were intravenously engrafted into B-NDG mice (female, 7-week-old, n=6). Human gastric cancer cell line NUGC4 (5E6) were inoculated subcutaneously 7days after PBMCs engraftment. AMG 910 (in house) was injected intraperitoneally 7 days after tumor inoculation. The animals were grouped into control and treatment when the tumor volume reached to 50-80 mm3 and the percentage of human blood hCD45+ cells ≥ 10%, at which time they were treated with drugs. (A) Schematic diagram of tumor model and drug delivery strategy; (B) Percentages of human CD45+ cells taken from peripheral blood on the day of administration (Day 0) and at the end point (Day 27); (C) Tumor volume; (D) Body weight. Results showed that the percentages of reconstituted human CD45+ cells continued to increase during administration. The anti-human CD3/CLDN18.2 bispecific antibody showed significant dose-dependent tumor suppression. B-NDG mice engrafted with human PBMCs can be used to establish tumor models and verify the efficacy of bispecific antibodies in vivo. Values are expressed as averages ±SEM.

A CDX orthotopic model for human colon cancer was established using human PBMCs engrafted B-NDG mice and the efficacy of anti-human PD-L1 antibody was verified. Human PBMCs (5E6) were intravenously engrafted into B-NDG mice (female, 7-week-old, n=6). Human colonic cancer cell line B-Tg(Luc) RKO cells (1E6) were orthotopically inoculated into colonic tissue of B-NDG mice 4 days after PBMCs engraftment. Atezolizumab (in house) was injected intraperitoneally 3 days after tumor inoculation. (A) Schematic diagram of tumor model and drug delivery strategy; (B) Imaging of mice to observe tumor growth; (B) Fluorescence intensity curve of tumor cells; (D) Body weight. Results showed that anti-human PD-L1 antibody significantly inhibited tumor growth in the orthotopic colon cancer model, demonstrating that B-NDG mice engrafted with human PBMCs can be used to establish colonic orthotopic tumor model and verify the efficacy of anti-human antibodies in vivo. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.

Engraftment of human PBMCs in B-NDG mice successfully constructed a graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) model. Human PBMCs (1E7) were intravenously engrafted into B-NDG mice 4 hrs after 1.0 Gy irradiation (female, 8-week-old, n=7/8). Mice were weighed twice a week and the health status of mice were recorded every day. Each mouse was scored according to the GvHD scoring standard. (A) Schematic diagram of the model-building strategy; (B) Survival curve; (C) Changes of body weight; (D) GvHD score. The results showed that the survival rate and the body weight of B-NDG mice were significantly reduced after irradiated and PBMC engraftment. GvHD scores were significant increased. But the GvHD symptoms vary between different donor sources of PBMCs. Therefor, B-NDG mice can be used to establish GvHD mouse model. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.

Engraftment of human PBMCs in B-NDG mice successfully constructed a graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) model and evaluated the efficacy of anti-human OX40 antibody. Human PBMCs (1E7) were intravenously engrafted into B-NDG mice 4 hrs after 1.0 Gy irradiation (female, 6-week-old, n=6). A anti-human OX40 antibody telazorlimab (in house) was intravenously injected into the mice of the treatment group. Mice were weighed three times a week and the health status of mice were recorded every day. Each mouse was scored according to the GvHD scoring standard. (A) Survival curve; (B) Changes of body weight; (C) GvHD score. The results showed that the GvHD model was successfully constructed. The survival rate, body weight and GvHD score of mice in the treatment group (telazorlimab) were significantly improved compared with those in the vehicle group. Therefor, B-NDG mice can be used to construct GvHD model and verify the efficacy of antibodies in vivo. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
Human immune system reconstitution with human CD34+ HSCs in B-NDG mice and efficacy evaluation
Engraftment of human CD34+ HSCs in B-NDG mice to reconstitute human immune system (adult mice)
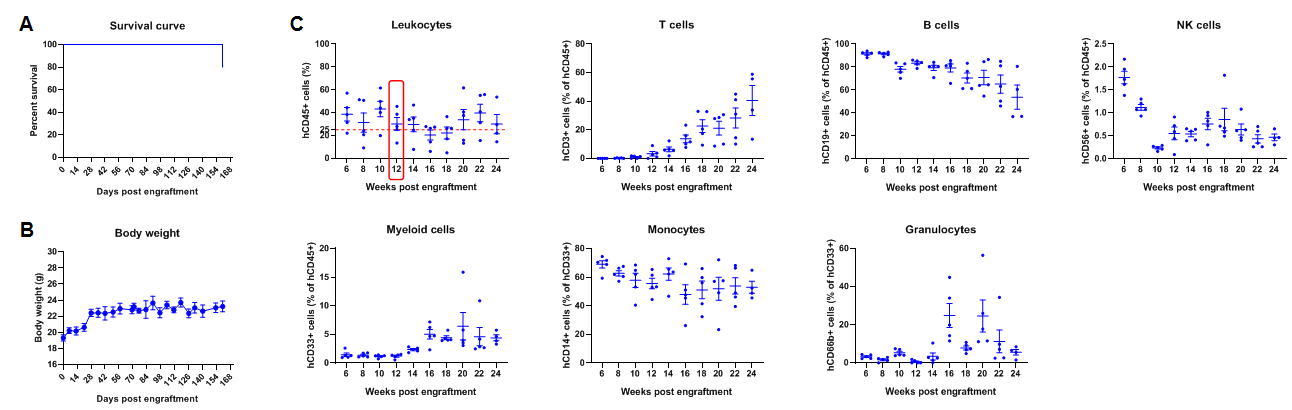
Engraftment of human CD34+ HSCs in adult B-NDG mice successfully reconstituted human T and B cells, a small number of NK and myeloid cells. Human CD34+ HSCs (1E5) were engrafted via the tail veins of B-NDG mice (female, 6-week-old, n=5) within 4-12 hours after being irradiated with 1.0 Gy of X-ray. The reconstitution level of human immune cells in peripheral blood was analyzed by flow cytometry. (A) Survival curve of human CD34+ HSCs engrafted mice; (B) Body weight; (C) Percentages of reconstituted human immune cells. The results showed that no mice died before 22 weeks of human CD34+ HSCs engraftment. Only one mouse died after 160 days of reconstitution. All the mice continued to gain body weight. The percentage of human CD45+ cells exceeded 25% at 6 weeks of reconstitution and can still be maintained at about 25% after 24 weeks of reconstitution. The percentage of human T cells begins to increase persistently at 10 weeks of reconstitution. The percentage of human B cells reached more than 90% at 6 weeks of reconstitution and continued to decline after 8 weeks. A small percentage of human NK cells, total myeloid cells, monocytes and granulocytes can also be detected throughout the reconstitution process.

Engraftment of human CD34+ HSCs in B-NDG mice to reconstitute human immune system (neonatal mice)

Engraftment of human CD34+ HSCs in neonatal B-NDG mice successfully reconstituted human T and B cells, a small number of NK and myeloid cells. Human CD34+ HSCs (1.5E5) were engrafted via the facial vein of B-NDG mice (male and female, 24-8 hour-old, n=28) within 4-12 hours after being irradiated with 0.8 Gy of X-ray. The reconstitution level of human immune cells in peripheral blood was analyzed by flow cytometry. (A) Survival curve of human CD34+ HSCs engrafted mice; (B) Body weight; (C) Percentages of reconstituted human immune cells; (D) Number of human immune cells. The results showed that the mice began to die from 17 weeks of reconstitution. But the lived mice continued to gain body weight. The percentage of human CD45+ cells exceeded 25% from 8 weeks of reconstitution. But there are obvious individual differences. The percentage of human T cells began to increase continuously at 10 weeks of reconstitution. Human CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells and Tregs could be detected at a relatively high level. The percentage of human B cells reached more than 70% at 6 weeks of reconstitution and continued to decline slowly after reaching the highest value at 8 weeks. A small percentage of human NK cells, total myeloid cells, monocytes and granulocytes can also be detected throughout the reconstitution process.
Publications
Suppression of MUC1-Overexpressing Tumors by a Novel MUC1/CD3 Bispecific Antibody.pdf
TLR8 agonist Motolimod-induced inflammatory death for treatment of acute myeloid leukemia.pdf
Establishing extended pluripotent stem cells from human urine cells.pdf










